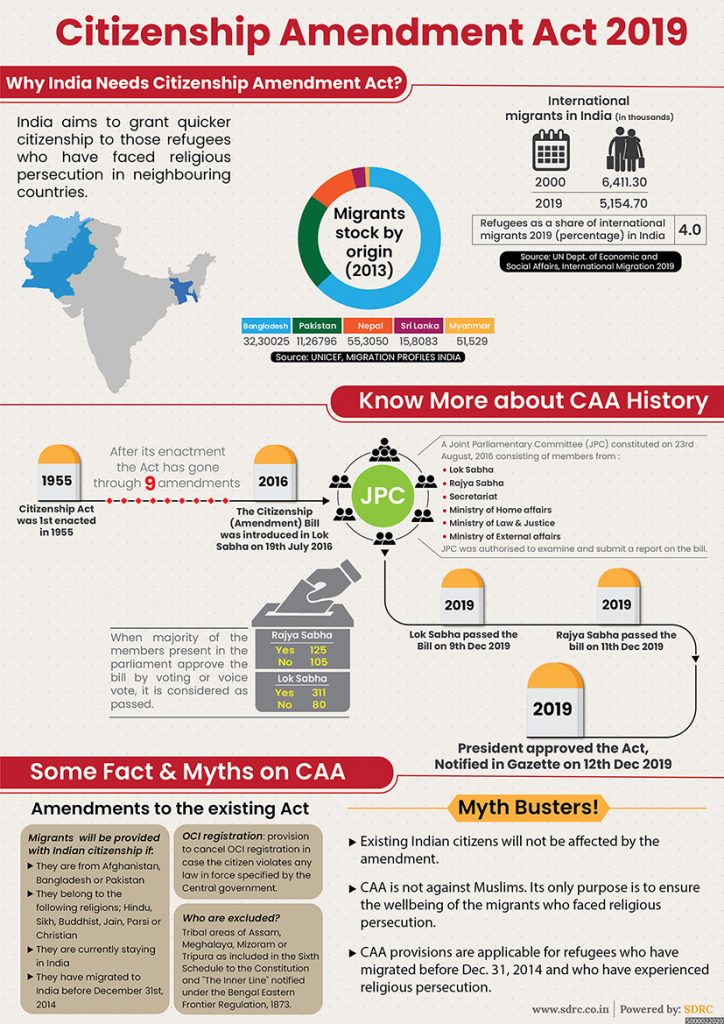
Through the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, India aims to grant quicker path to citizenship to those refugees who have faced religious persecution in neighboring countries.
Migrants will be provided with Indian citizenship if:
- They are from Afghanistan, Bangladesh or Pakistan.
- The belong to the following religions: Hinduism, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism, Zoroastrianism, or Christianity.
- They are currently staying in India.
- They have migrated to India before December 31st, 2014.
As per UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, International Migration 2019, there were 6,41,1300 international migrants in India in 2000, where as their number stood at 5154700 in 2019.
The percentage of refugees as a share of international migrants 2019 in India stood at 4%.
Some of the myth busters:
* Existing Indian citizens will not be affected by the amendment.
* The Act is not against any religion. Its sole purpose is to ensure the well-being of migrants who faced religious persecution.
* CAA provisions are applicable for refugees who have migrated before Dec. 31, 2014 because of religious persecution.
Under the CAA, tribal areas of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram or Tripura are excluded as per the Sixth Schedule to the constitutions and the inner line notified under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1973.